2026
 VideoMind: A Chain-of-LoRA Agent for Temporal-Grounded Video ReasoningInternational Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026LAW Workshop @ NeurIPS (Spotlight), 2025
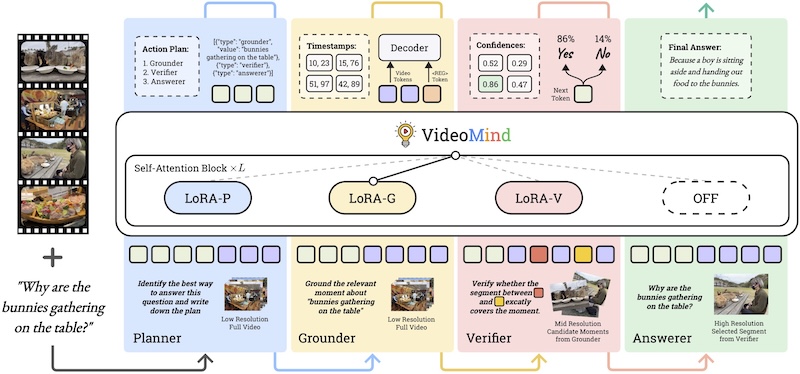
VideoMind: A Chain-of-LoRA Agent for Temporal-Grounded Video ReasoningInternational Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026LAW Workshop @ NeurIPS (Spotlight), 2025Videos, with their unique temporal dimension, demand precise grounded understanding, where answers are directly linked to visual, interpretable evidence. Despite significant breakthroughs in text-based reasoning with large language models, multi-modal reasoning – especially for videos – remains limited. In this work, we fill this gap by introducing VideoMind, a novel video-language agent for temporal-grounded video reasoning. Our method involves two key innovations: (1) We identify four essential capabilities for grounded video reasoning and propose a role-based agentic workflow, comprising a planner to coordinate roles, a grounder for temporal event localization, a verifier to assess event candidates, and an answerer for question answering. (2) To efficiently integrate these roles during inference, we propose a novel Chain-of-LoRA mechanism, where a unified base model with multiple LoRA adapters is leveraged to enable seamless role switching, balancing efficiency and flexibility. Extensive experiments on 14 benchmarks across 3 tasks, including Grounded VideoQA, Video Temporal Grounding, and General VideoQA, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme in advancing video agent, test-time scaling, and long-form video reasoning.
2025
 UniPixel: Unified Object Referring and Segmentation for Pixel-Level Visual ReasoningAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
UniPixel: Unified Object Referring and Segmentation for Pixel-Level Visual ReasoningAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025Recent advances in Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated their remarkable success as general-purpose multi-modal assistants, with particular focuses on holistic image- and video-language understanding. Conversely, less attention has been given to scaling fine-grained pixel-level understanding capabilities, where the models are expected to realize pixel-level alignment between visual signals and language semantics. Some previous studies have applied LMMs to related tasks such as region-level captioning and referring expression segmentation. However, these models are limited to performing either referring or segmentation tasks independently and fail to integrate these fine-grained perception capabilities into visual reasoning. To bridge this gap, we propose UniPixel, a large multi-modal model capable of flexibly comprehending visual prompt inputs and generating mask-grounded responses. Our model distinguishes itself by seamlessly integrating pixel-level perception with general visual understanding capabilities. Specifically, UniPixel processes visual prompts and generates relevant masks on demand, and performs subsequent reasoning conditioning on these intermediate pointers during inference, thereby enabling fine-grained pixel-level reasoning. The effectiveness of our approach has been verified on 10 benchmarks across a diverse set of tasks, including pixel-level referring/segmentation and object-centric understanding in images/videos. A novel PixelQA task that jointly requires referring, segmentation, and question answering is also designed to verify the flexibility of our method.
 A Survey on Video Temporal Grounding with Multimodal Large Language ModelIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2025
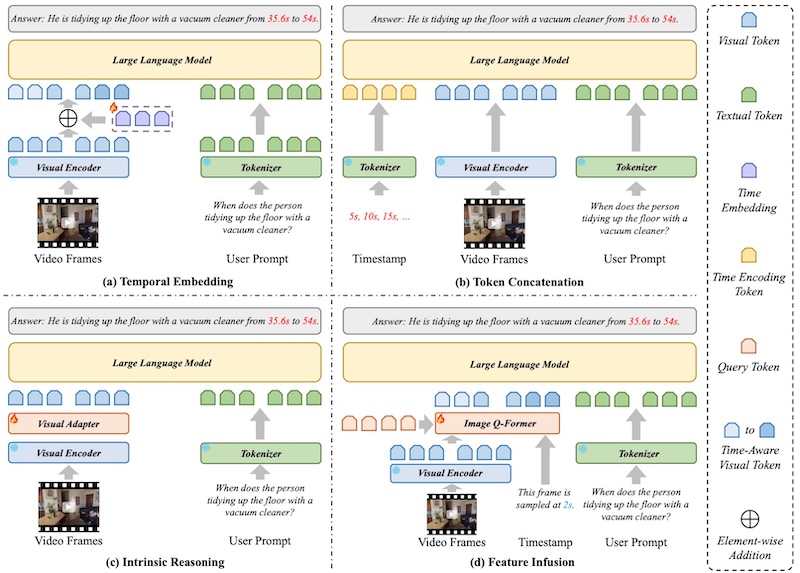
A Survey on Video Temporal Grounding with Multimodal Large Language ModelIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2025The recent advancement in video temporal grounding (VTG) has significantly enhanced fine-grained video understanding, primarily driven by multimodal large language models (MLLMs). With superior multimodal comprehension and reasoning abilities, VTG approaches based on MLLMs (VTG-MLLMs) are gradually surpassing traditional fine-tuned methods. They not only achieve competitive performance but also excel in generalization across zero-shot, multi-task, and multi-domain settings. Despite extensive surveys on general video-language understanding, comprehensive reviews specifically addressing VTG-MLLMs remain scarce. To fill this gap, this survey systematically examines current research on VTG-MLLMs through a three-dimensional taxonomy: 1) the functional roles of MLLMs, highlighting their architectural significance; 2) training paradigms, analyzing strategies for temporal reasoning and task adaptation; and 3) video feature processing techniques, which determine spatiotemporal representation effectiveness. We further discuss benchmark datasets, evaluation protocols, and summarize empirical findings. Finally, we identify existing limitations and propose promising research directions.
 VisionMath: Vision-Form Mathematical Problem-SolvingThe IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025
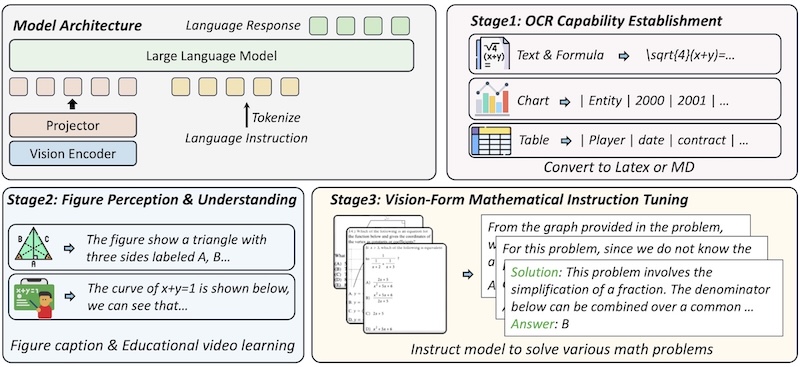
VisionMath: Vision-Form Mathematical Problem-SolvingThe IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025Mathematical problems in real-world scenarios are often presented in a purely vision-form, where textual problem statement and accompanying math figures, e.g., geometry figures and functional graphs, are integrated into a single image. This vision-form problem-solving task requires precise comprehension and reasoning on both textual and graphical elements in the images, posing significant challenge to current Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), which process text and math figures in isolation. In this work, we propose VisionMath, the first exploration for vision-form mathematical problem-solving model, which employs a three-stage progressive multimodal reasoning alignment strategy to systematically enhance task-specific capabilities. Building upon a LLM proficient in unimodal mathematical reasoning, VisionMath first establishes foundational OCR capabilities through capturing rendered mathematical problem images. Subsequently, the model develops comprehensive understanding of figure structures and properties via learning from figure descriptions and mathematical educational videos. Finally, the model’s reasoning capacity is activated using carefully constructed visual-form problem-solving datasets VisionMath-IT with chain-of-thought annotations. For comprehensive evaluation, we construct multilingual benchmarks covering diverse problem types, including geometry, algebra, function problems in both English and Chinese.
 Affordance-Aware Object Insertion via Mask-Aware Dual DiffusionP13N: Personalization in Generative AI @ ICCV, 2025
Affordance-Aware Object Insertion via Mask-Aware Dual DiffusionP13N: Personalization in Generative AI @ ICCV, 2025As a common image editing operation, image composition involves integrating foreground objects into background scenes. In this paper, we expand the application of the concept of Affordance from human-centered image composition tasks to a more general object-scene composition framework, addressing the complex interplay between foreground objects and background scenes. Following the principle of Affordance, we define the affordance-aware object insertion task, which aims to seamlessly insert any object into any scene with various position prompts. To address the limited data issue and incorporate this task, we constructed the SAM-FB dataset, which contains over 3 million examples across more than 3,000 object categories. Furthermore, we propose the Mask-Aware Dual Diffusion (MADD) model, which utilizes a dual-stream architecture to simultaneously denoise the RGB image and the insertion mask. By explicitly modeling the insertion mask in the diffusion process, MADD effectively facilitates the notion of affordance. Extensive experimental results show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods and exhibits strong generalization performance on in-the-wild images.
2024
 E.T. Bench: Towards Open-Ended Event-Level Video-Language UnderstandingAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024
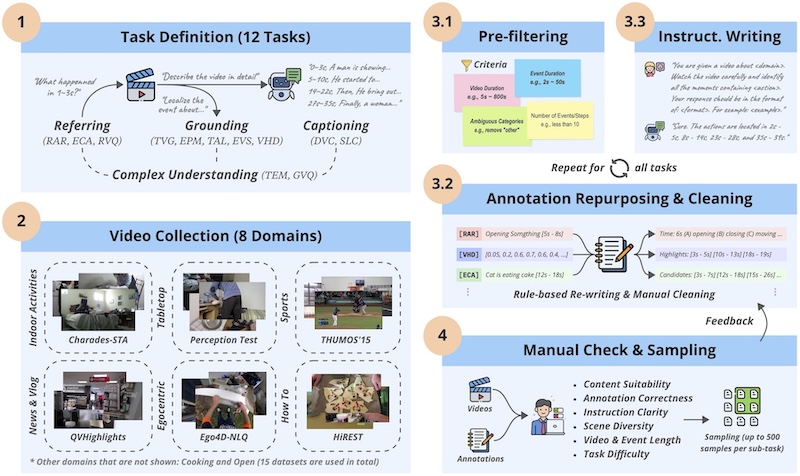
E.T. Bench: Towards Open-Ended Event-Level Video-Language UnderstandingAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2024Recent advances in Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) have demonstrated their great potential in general-purpose video understanding. To verify the significance of these models, a number of benchmarks have been proposed to diagnose their capabilities in different scenarios. However, existing benchmarks merely evaluate models through video-level question-answering, lacking fine-grained event-level assessment and task diversity. To fill this gap, we introduce E.T. Bench (Event-Level & Time-Sensitive Video Understanding Benchmark), a large-scale and high-quality benchmark for open-ended event-level video understanding. Categorized within a 3-level task taxonomy, E.T. Bench encompasses 7.3K samples under 12 tasks with 7K videos (251.4h total length) under 8 domains, providing comprehensive evaluations. We extensively evaluated 8 Image-LLMs and 12 Video-LLMs on our benchmark, and the results reveal that state-of-the-art models for coarse-level (video-level) understanding struggle to solve our fine-grained tasks, e.g., grounding event-of-interests within videos, largely due to the short video context length, improper time representations, and lack of multi-event training data. Focusing on these issues, we further propose a strong baseline model, E.T. Chat, together with an instruction-tuning dataset E.T. Instruct 164K tailored for fine-grained event-level understanding. Our simple but effective solution demonstrates superior performance in multiple scenarios.
 R2-Tuning: Efficient Image-to-Video Transfer Learning for Video Temporal GroundingThe European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2024
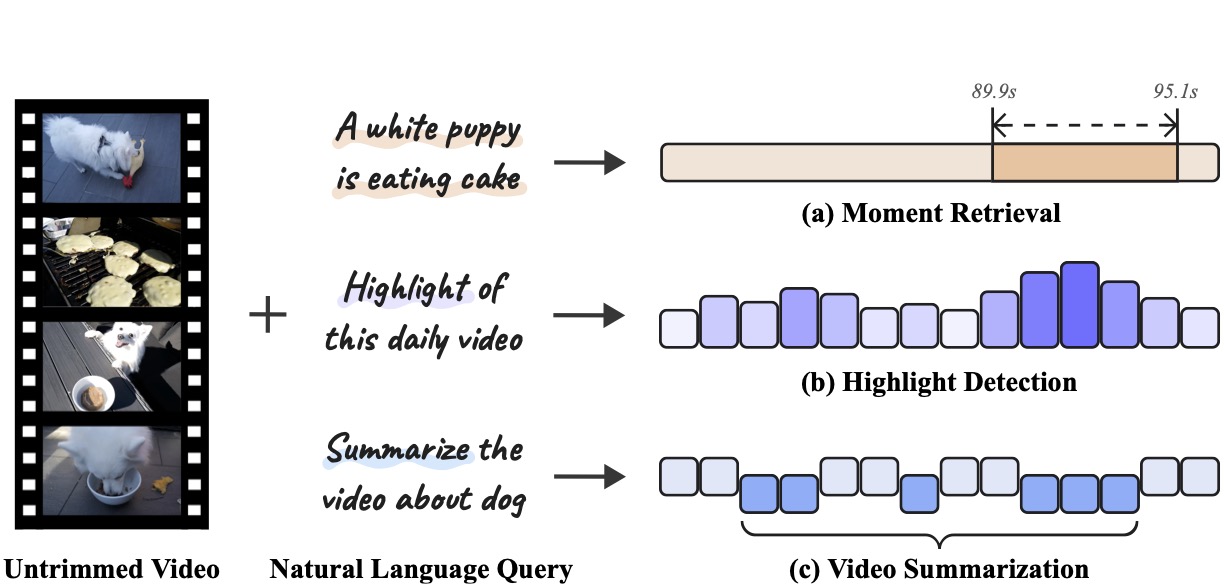
R2-Tuning: Efficient Image-to-Video Transfer Learning for Video Temporal GroundingThe European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2024Video temporal grounding (VTG) is a fine-grained video understanding problem that aims to ground relevant clips in untrimmed videos given natural language queries. Most existing VTG models are built upon frame-wise final-layer CLIP features, aided by additional temporal backbones (e.g., SlowFast) with sophisticated temporal reasoning mechanisms. In this work, we claim that CLIP itself already shows great potential for fine-grained spatial-temporal modeling, as each layer offers distinct yet useful information under different granularity levels. Motivated by this, we propose Reversed Recurrent Tuning (R^2-Tuning), a parameter- and memory-efficient transfer learning framework for video temporal grounding. Our method learns a lightweight R^2 Block containing only 1.5% of the total parameters to perform progressive spatial-temporal modeling. Starting from the last layer of CLIP, R^2 Block recurrently aggregates spatial features from earlier layers, then refines temporal correlation conditioning on the given query, resulting in a coarse-to-fine scheme. R^2-Tuning achieves state-of-the-art performance across three VTG tasks (i.e., moment retrieval, highlight detection, and video summarization) on six public benchmarks (i.e., QVHighlights, Charades-STA, Ego4D-NLQ, TACoS, YouTube Highlights, and TVSum) even without the additional backbone, demonstrating the significance and effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
 Learning to Aggregate Multi-Scale Context for Instance Segmentation in Remote Sensing ImagesIEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS), 2024
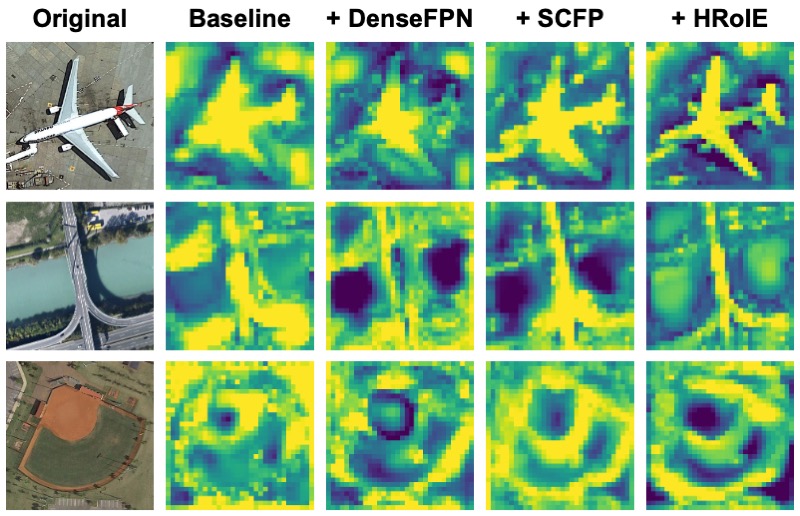
Learning to Aggregate Multi-Scale Context for Instance Segmentation in Remote Sensing ImagesIEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS), 2024The task of instance segmentation in remote sensing images, aiming at performing per-pixel labeling of objects at instance level, is of great importance for various civil applications. Despite previous successes, most existing instance segmentation methods designed for natural images encounter sharp performance degradations when they are directly applied to top-view remote sensing images. Through careful analysis, we observe that the challenges mainly come from the lack of discriminative object features due to severe scale variations, low contrasts, and clustered distributions. In order to address these problems, a novel context aggregation network (CATNet) is proposed to improve the feature extraction process. The proposed model exploits three lightweight plug-and-play modules, namely dense feature pyramid network (DenseFPN), spatial context pyramid (SCP), and hierarchical region of interest extractor (HRoIE), to aggregate global visual context at feature, spatial, and instance domains, respectively. DenseFPN is a multi-scale feature propagation module that establishes more flexible information flows by adopting inter-level residual connections, cross-level dense connections, and feature re-weighting strategy. Leveraging the attention mechanism, SCP further augments the features by aggregating global spatial context into local regions. For each instance, HRoIE adaptively generates RoI features for different downstream tasks. Extensive evaluations of the proposed scheme on iSAID, DIOR, NWPU VHR-10, and HRSID datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-arts under similar computational costs.
2023
 Timestamps as Prompts for Geography-Aware Location RecommendationThe ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2023
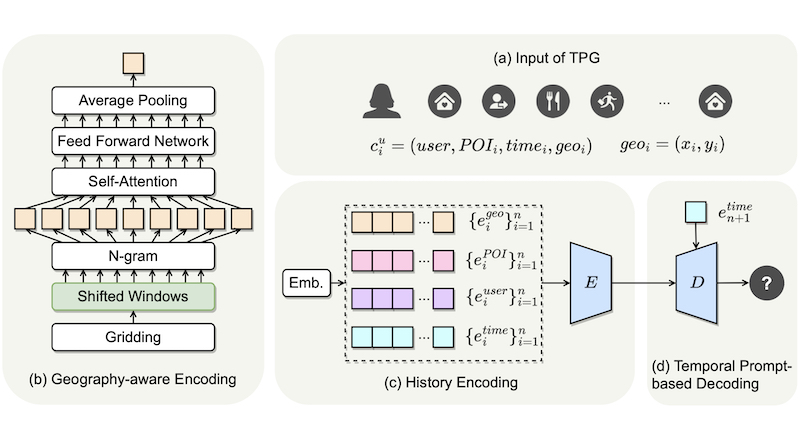
Timestamps as Prompts for Geography-Aware Location RecommendationThe ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM), 2023Location recommendation plays a vital role in improving users’ travel experience. The timestamp of the POI to be predicted is of great significance, since a user will go to different places at different times. However, most existing methods either do not use this kind of temporal information, or just implicitly fuse it with other contextual information. In this paper, we revisit the problem of location recommendation and point out that explicitly modeling temporal information is a great help when the model needs to predict not only the next location but also further locations. In addition, state-of-the-art methods do not make effective use of geographic information and suffer from the hard boundary problem when encoding geographic information by gridding. To this end, a Temporal Prompt-based and Geography-aware (TPG) framework is proposed. The temporal prompt is firstly designed to incorporate temporal information of any further check-in. A shifted window mechanism is then devised to augment geographic data for addressing the hard boundary problem. Via extensive comparisons with existing methods and ablation studies on five real-world datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method under various settings. Most importantly, our proposed model has the superior ability of interval prediction. In particular, the model can predict the location that a user wants to go to at a certain time while the most recent check-in behavioral data is masked, or it can predict specific future check-in (not just the next one) at a given timestamp.
 End-to-End Personalized Next Location Recommendation via Contrastive User Preference ModelingIEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (TCSS), 2023
End-to-End Personalized Next Location Recommendation via Contrastive User Preference ModelingIEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (TCSS), 2023Predicting the next location is a highly valuable and common need in many location-based services such as destination prediction and route planning. The goal of next location recommendation is to predict the next Point-of-Interest (POI) a user might go to based on user’s historical trajectory. Most existing models learn mobility patterns merely from users’ historical check-in sequences while overlooking the significance of user preference modeling. In this work, a novel Point-of-Interest Transformer (POIFormer) with contrastive user preference modeling is developed for end-to-end next location recommendation. This model consists of three major modules: history encoder, query generator, and preference decoder. History encoder is designed to model mobility patterns from historical check-in sequences, while query generator explicitly learns user preferences to generate user-specific intention queries. Finally, preference decoder combines the intention queries and historical information to predict the user’s next location. Extensive comparisons with representative schemes and ablation studies on four real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed scheme under various settings. In addition, we further investigate the factors that enable contrastive learning to work effectively in the context of human mobility and conclude that both the category and quantity of POIs influence the performance of contrastive learning.
2022
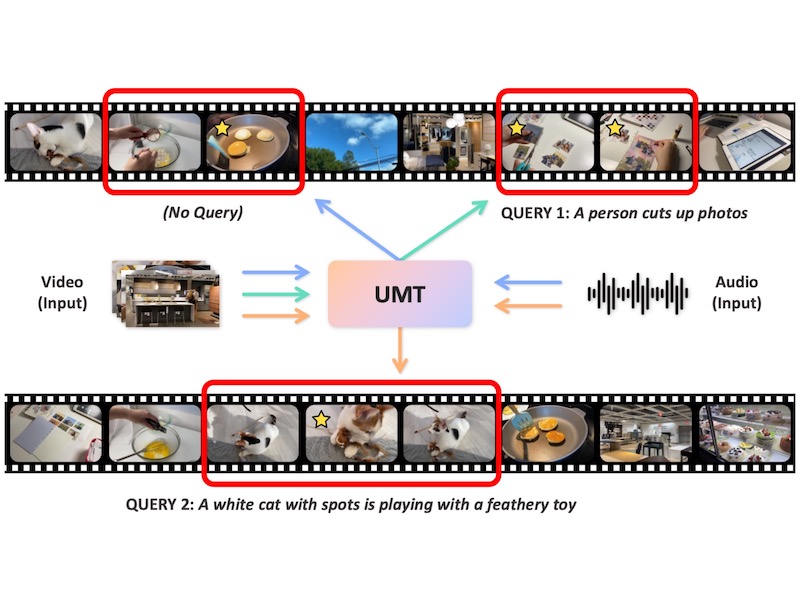 UMT: Unified Multi-modal Transformers for Joint Video Moment Retrieval and Highlight DetectionThe IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2022
UMT: Unified Multi-modal Transformers for Joint Video Moment Retrieval and Highlight DetectionThe IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2022Finding relevant moments and highlights in videos according to natural language queries is a natural and highly valuable common need in the current video content explosion era. Nevertheless, jointly conducting moment retrieval and highlight detection is an emerging research topic, even though its component problems and some related tasks have already been studied for a while. In this paper, we present the first unified framework, named Unified Multi-modal Transformers (UMT), capable of realizing such joint optimization while can also be easily degenerated for solving individual problems. As far as we are aware, this is the first scheme to integrate multi-modal (visual-audio) learning for either joint optimization or the individual moment retrieval task, and tackles moment retrieval as a keypoint detection problem using a novel query generator and query decoder. Extensive comparisons with existing methods and ablation studies on QVHighlights, Charades-STA, YouTube Highlights, and TVSum datasets demonstrate the effectiveness, superiority, and flexibility of the proposed method under various settings.
2020
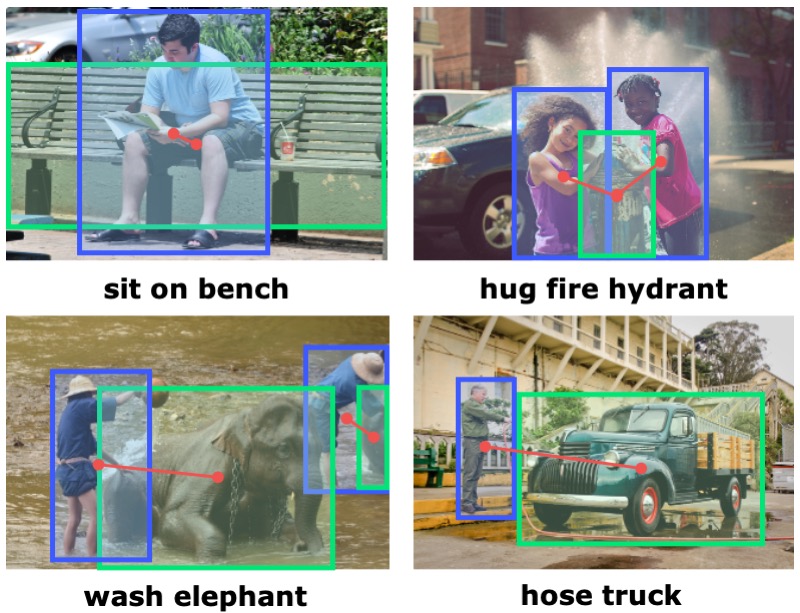 ConsNet: Learning Consistency Graph for Zero-Shot Human-Object Interaction DetectionThe ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), 2020
ConsNet: Learning Consistency Graph for Zero-Shot Human-Object Interaction DetectionThe ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), 2020We consider the problem of Human-Object Interaction (HOI) Detection, which aims to locate and recognize HOI instances in the form of <human, action, object> in images. Most existing works treat HOIs as individual interaction categories, thus can not handle the problem of long-tail distribution and polysemy of action labels. We argue that multi-level consistencies among objects, actions and interactions are strong cues for generating semantic representations of rare or previously unseen HOIs. Leveraging the compositional and relational peculiarities of HOI labels, we propose ConsNet, a knowledge-aware framework that explicitly encodes the relations among objects, actions and interactions into an undirected graph called consistency graph, and exploits Graph Attention Networks (GATs) to propagate knowledge among HOI categories as well as their constituents. Our model takes visual features of candidate human-object pairs and word embeddings of HOI labels as inputs, maps them into visual-semantic joint embedding space and obtains detection results by measuring their similarities. We extensively evaluate our model on the challenging V-COCO and HICO-DET datasets, and results validate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-arts under both fully-supervised and zero-shot settings.